So First, let's go through the basic understanding of Programming and Programming Languages in general and without this you don't get the idea of what I am talking about, So let's Begin.
What is Programming and Programming Language in general?

Programming is a set of instructions that a computer can follow to perform a certain task.
For example, sending a WhatsApp message to a friend, sending a formal email to our employer or even searching for a restaurant near you using Google Maps,
We can do all this with the help of programming.
In this digital world everything is made with the use of programming.
 Programming Languages is a way to write the programming instruction(known as source code) for the computer. for e.x., we humans use Language to communicate with the other person. Just like that, we use a programming language to communicate with computers.
Programming Languages is a way to write the programming instruction(known as source code) for the computer. for e.x., we humans use Language to communicate with the other person. Just like that, we use a programming language to communicate with computers.
Types of Programming languages
There are 3 types of programming languages
- Low-Level Language
- High-Level Language
- Middle-Level Language
1) Low-Level Programming Language is a machine-dependent language, what does that mean? it means the computers only understand the (0s & 1s) binary system.
Binary (or base-2) is a numeric system that only uses two digits — 0 and 1.
if the program uses low-level language then it doesn't need any translator(We will see in a Translator sector) and for that reason, the execution of the program is very fast.
The low-level language is further divided into two parts:
- Machine-Language
- Assembly Language
Machine Language is also known as machine code or object code. So, programs don't need to translate Because the Computer understands the machine language(0s & 1s) i.e. it is faster than the High-level programming Language.
Assembly Language, it represents the instructions(source code) in a Symbolic and human-understandable form. It uses the assembler to convert the Assembly language to machine language.
2) High-Level Programming Language or HLL is specially designed for beginner programmers(who can write the source code)who just started the programming as well as the normal person who didn't understand the programming for developing the user-friendly software programs.
HLL requires the Translator(compiler & interpreter) to translate the HLL source code into the machine language(object code) for the execution purpose Because the computer understands only the Binary system(0s & 1s).
HLL is Very popular among programmers because it's easy to read, write & maintain.
3)Middle-Level Programming Language (MLPL) lies between low-level and high-level language. so it supports both high level & low-level features.
Translators in the Programming World
Suppose, you go to another country to visit. You come out of the country airport, and then you start asking a cab driver to drive you around, but the problem is the cab driver doesn't understand your language because his native language is different, then another person at that time comes and has a good understanding of both the languages, then he begins to explain each other's language to both of them, what they want to convey to each other. so, the person who came and helps them in their languages is called a translator (the person who knows many languages and converts them into another language).
So, Let's Extend this example and try to understand the context behind the translator in Programming World.
so in the previous example, we have three persons Traveller, Cab driver and the Translator.
Let's connect the dots:-
In the programming World,
- Traveller is nothing But our Source Code(instructions)
- Stranger is a computer that understands only the binary system(0s & 1s).
- Translator is the program that translates the High-Level Language into the Low-Level Language.
Types Of Translators:- There are 3 different types of Translators:
- Compiler it scans the Whole Program at once and translate it into machine code and it reports an error after the conversion that detects while scanning.
- Interpreter- On the Other Hand, the Interpreter Do the same thing just like the Compiler do, translating the High-Level Language into Low-Level Language but the interpreter took the line by line instructions and it reports an error while doing the conversion.
- Assembler is translate the Assembly Language into the machine code.
There are lots of programming languages are developed, a few of them are very popular and one of them is Python.
Python

What is Python?
Python is a General-purpose, Multi-paradigm, Interpreted( Programming Language. what does that mean?
look at the statement, python is a "General Purpose", general-purpose means you can build pretty much everything with python and multi-paradigm means you can write source code In multiple ways like as using procedural programming, structural programming and object-oriented programming (don't bother with this, we will see in the next blogs)
Types of Apps:-
Following is the list of apps that you can build using python.
- Console App (terminal app like c & c++)
- Desktop App (like windows calculator app)
- Web Apps
- Mobile Apps
- IoT Apps
History:-
- Python is created by Guido Van Rossum at CWI

CWI: The Centrum Wiskunde & Informatica is a research centre in the field of mathematics and theoretical computer science.
- Idea of Python is Started in the early 1980s and real implementation started in Dec 1989.
- In 1991[27 Feb 1991] Guido Van Rossum Published the code (labelled version 0.9.0)
- Official 1st version released in 1994.
Reasons Behind the Python Success:
- It Is an open-source software.
Open source software is code that is designed to be publicly accessible—anyone can see, modify, and distribute the code as they see fit.
- Very simple, straightforward syntax
- Dynamically strong Typed language( You don't need to explicitly declare variable types.)
- It is an object-oriented Language
- it uses indentation in place of curly braces that way it gives more readability.
How does Python works?
Note: whenever I say python I implicitly want to say, python interpreter.
As of now, we get the sense of every programming language needs a translator (compiler or interpreter) to translate from High-level language to Low-level language(language that computers understand), and python is an interpreted language. Now let see how python interpreter works.
- This is the python official website, for downloading the latest python interpreter.
The link is down below:
- when you download from the above site, you actually download the CPython.
The link is down below:
What exactly is CPython?
- CPython is a python that is written in c.
- It is the main implementation that Guido Van Rossum released in 1991.
- CPython can be defined as both an interpreter and a compiler as it compiles Python code into bytecode before interpreting it.
- there are many other python projects are there: PyPy(build interpreter using python), Jython(Java Python), IronPython(using .net framework) and many more.
Let see the python program execution.
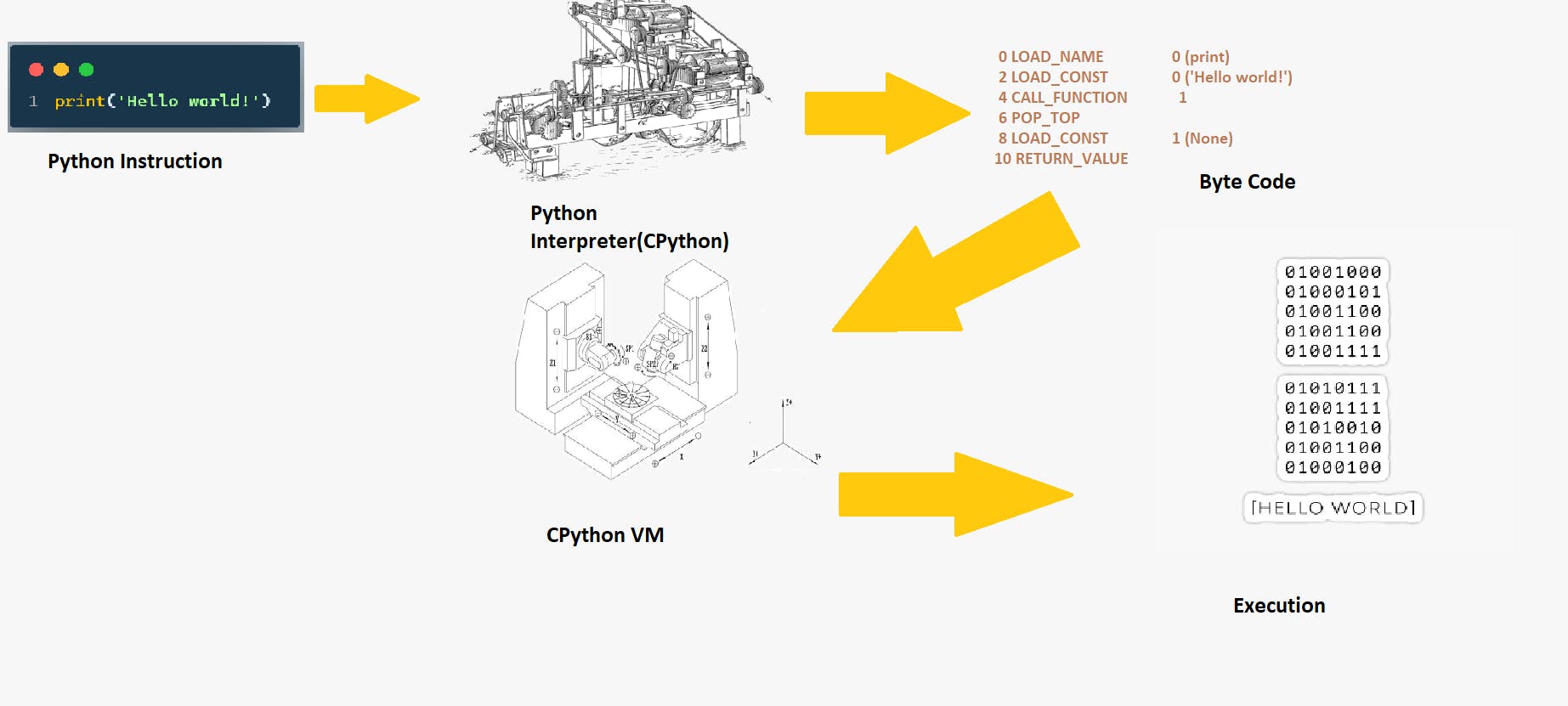
Whenever we create the python file it Ended with the .py extension for e.x. filename is helloWorld .py
As we know, To Run any instructions on a computer we need a Translator(Compiler or Interpreter).
- So same applies here, For executing the HelloWorld file we need a Translator and in our case that is CPython(Python interpreter).
When we run the python file it goes to the CPython(Python interpreter) and creates a ByteCode( very near to the machine code)
0 LOAD_NAME 0 (print) 2 LOAD_CONST 0 ('Hello world!') 4 CALL_FUNCTION 1 6 POP_TOP 8 LOAD_CONST 1 (None) 10 RETURN_VALUEAfter that this ByteCode sends to the CPython VM that creates a machine code and execute it on the machine.
For More Information About CPython Implementation I'll Attach the Link Below Python behind the scenes #1: how the CPython VM works


